Mainframe modernization, upgrade cadence, and tooling decisions are shaped as much by workforce structure as by technology. The 2026 survey reflects a notable shift in respondent mix while reinforcing continuity in operating models.
Importantly, the 2026 workforce findings must be interpreted carefully. Changes in experience distribution reflect participation patterns rather than evidence of industry-wide workforce disruption.
Experience Levels and Workforce Composition
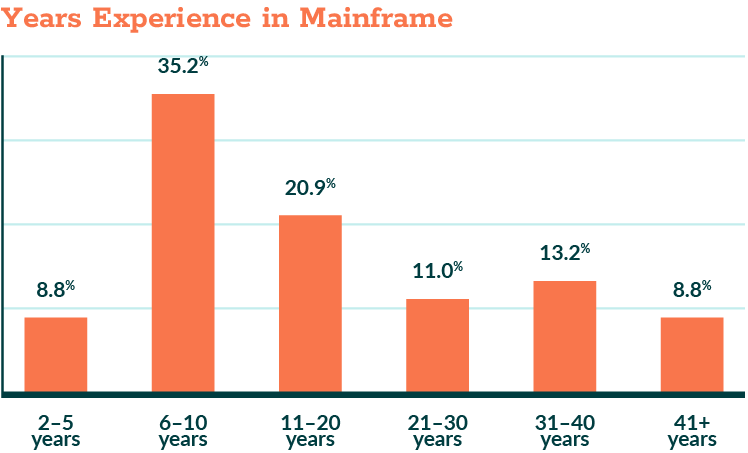
This year’s respondent profile differs markedly from that in 2025. In contrast to last year, when professionals with more than 30 years of experience dominated responses, 2026 is led by mid-career practitioners. The largest cohorts fall within the 6–10-year and 11–20-year ranges.
This shift likely reflects survey participation patterns rather than evidence of large-scale retirement or workforce turnover. What remains consistent is that respondents report meaningful tenure and operational responsibility. The change is not necessarily about workforce stability.
Figure 5.1: Years of Experience in Mainframe (2026)
Question: How many years have you been employed in mainframe-related positions?
Multi-Role Responsibilities and Consolidated Expertise
While the distribution of experience shifted, multi-role responsibility patterns did not.
A significant portion of the 2026 respondents report holding two or more functional roles spanning systems administration, systems programming, database management, performance, and security. A smaller but meaningful subset continues to report three or more concurrent responsibilities.
The results highlight the ongoing trend of multi-disciplinary mainframe roles:
- Nearly one-third of respondents report holding two or more technical roles.
- A smaller but notable group balances three or more responsibilities.
- For example, system administrators frequently serve as system programmers, and a significant subset also assumes security responsibilities.
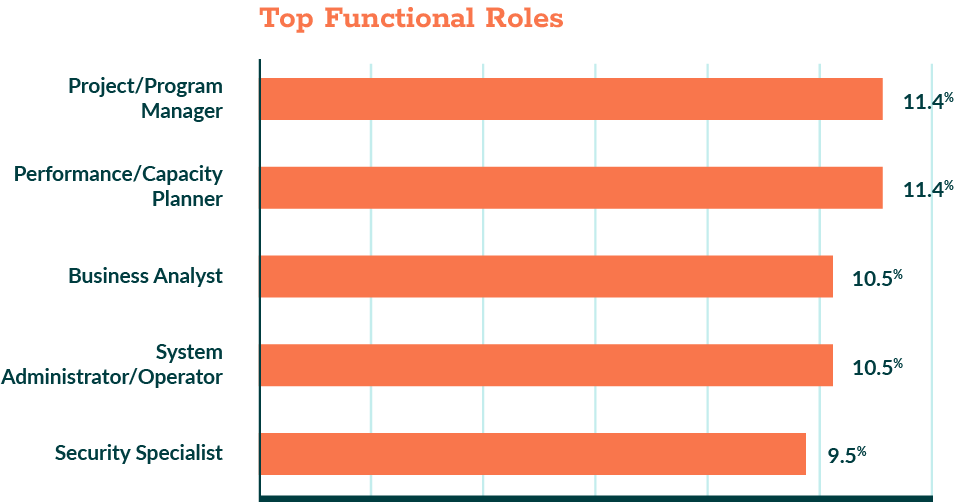
Figure 5.2: Top Functional Roles (2026)
Question: What is your role in the organization?
Selected Roles in the Organization
| 1 | Performance / Capacity Planner | 11.4% |
| 2 | Project / Program Manager | 11.4% |
| 3 | System Administrator / Operator | 10.5% |
| 4 | Business Analyst | 10.5% |
| 5 | Security Specialist | 9.5% |
| 6 | Application Developer / Programmer | 8.6% |
| 7 | Database Administrator (Db2, IMS, etc) | 8.6% |
| 8 | IT Manager / Decision Maker | 7.6% |
| 9 | Executive / Leadership (CEO, CTO, VP) | 5.7% |
| 10 | QA / Testing Specialist | 4.8% |
| 11 | Trainer / Educator / Technical Writer | 4.8% |
| 12 | Vendor Engineer / Parnter Representitive | 2.9% |
| 13 | Other | 1.9% |
Figure 5.2: Top Functional Roles (2026)
Question: What is your role in the organization?
This reinforces a consistent theme from the previous 2025 Arcati report: mainframe professionals are rarely narrow specialists. Instead, they are multi-skilled technologists responsible for operating, securing, optimizing, and evolving deeply interconnected systems. This concentration of responsibility has downstream implications, which are explored later in this report.
Staffing Stability and Change Management
Despite persistent industry discussion around skills shortages, there is no evidence of widespread staffing disruption. Instead, workforce considerations appear to influence how change is executed, not whether it occurs.
Organizations continue to favor:
- Incremental modernization
- Staged upgrades
- Conservative risk management
Unlike in prior years, the 2026 data do not support claims of a stable experience distribution across survey cycles. Stability appears in operating models, not in respondent tenure profiles.
Training, Knowledge Transfer, and Concentrated Expertise
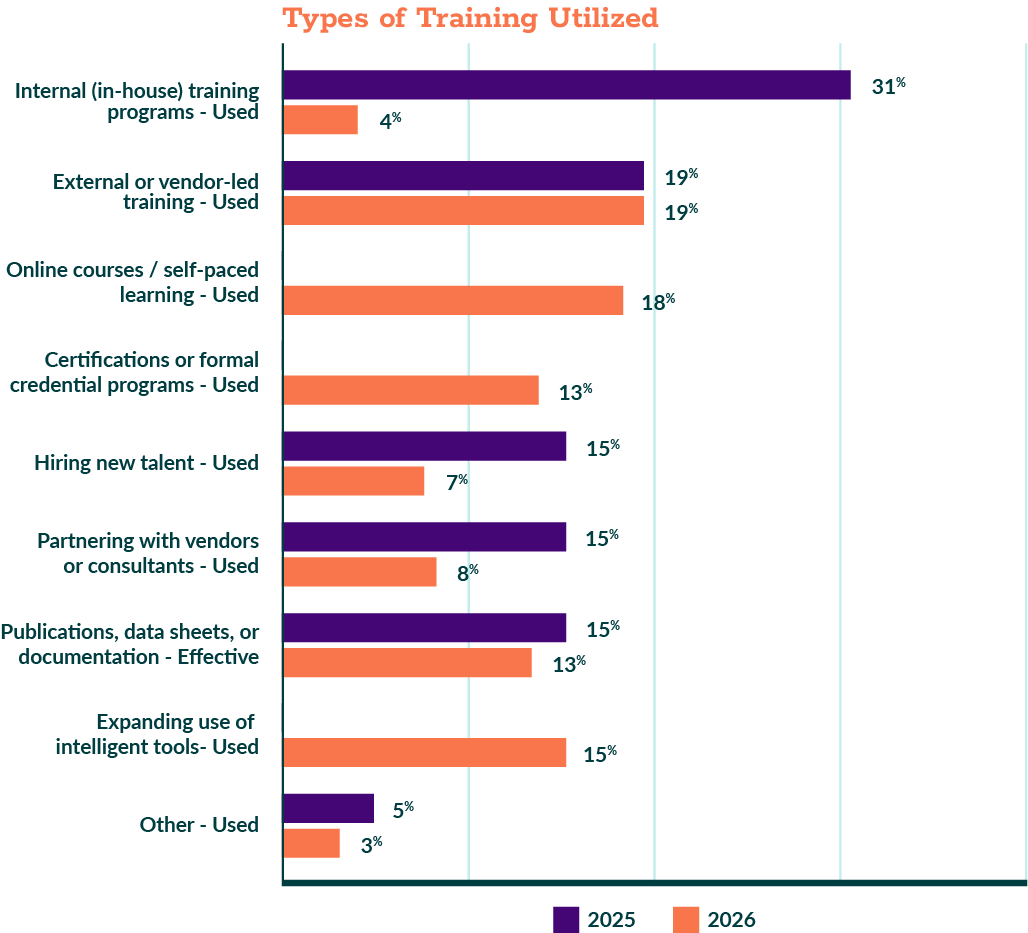
Training and knowledge transfer remain visible priorities. Organizations report using internal programs, vendor training, online courses, certifications, and selective hiring to address skill gaps. Access to learning pathways appears broader than in earlier Arcati surveys.
Figure 5.3: Reported Approaches to Mainframe Training and Skill Development (2025–2026)
Question: How do you address skill gaps in your mainframe team? (Select all that apply)
Figure 5.4: Effectiveness of Approaches to Mainframe Training and Skill Development (2026)
Question: How do you address skill gaps in your mainframe team? (Select all that apply)
However, responsibility for high-impact decisions remains with experienced staff. System-of-record changes, performance tuning, and security configuration are not broadly distributed tasks. Skill development appears layered. Newer practitioners gain capability over time, often working alongside senior team members before operating independently.
The data suggest an expansion of participation, not a redistribution of authority.
The survey highlights skills gaps affecting approximately 39% of respondents in areas such as security, integration, and hybrid environments. At ASPG, we see this as a call to action for structured upskilling programs, vendor-led certifications, and mentoring initiatives that empower teams to master modern security tools while leveraging the mainframe’s reliability. Rather than a “talent cliff,” we view this as a transitional phase where experience and emerging skills are converging to sustain productivity and continuity.
Operating Models in Practice
When viewed alongside experience and role data, a clear operating pattern emerges. Mainframe environments are typically supported by lean teams with broad responsibilities. Individual jobs often span systems, databases, performance, and security domains rather than working within narrow silos.
These teams maintain high availability while supporting integration, modernization, and optimization. The workforce data does not indicate stagnation. It indicates controlled change within defined constraints.
Workforce Patterns Over Time
Across recent Arcati survey cycles, workforce characteristics show less volatility than usage trends or technology adoption. Role consolidation persists, and responsibility remains concentrated.
This continuity helps explain why modernization is measured rather than treated as an abrupt transition. Workforce realities shape the pace and structure of change. As environments become more integrated, pressure increases on small, experienced teams.
The next section examines how tooling and automation are absorbing that complexity.





0 Comments