In this session of the Mainframe Virtual User Groups, Broadcom Distinguished Engineer Chris Crone provided a practical walkthrough of SQL and SQL PL enhancements across Db2 12 and Db2 13. Drawing on 35 years of experience working in Db2 internals, including SQL parsing, optimization, and architectural design, Chris explained not just what changed, but how these enhancements influence real-world performance and application behavior.
Db2 12: Strengthening Core SQL & SQL PL Capabilities (~00:03–00:20)
Db2 12 introduced a broad set of enhancements that modernize application behavior and align Db2 more closely with SQL standards. Chris began by explaining how new pagination options evolved to meet developer expectations and reduce dependence on older cursor-based techniques.
Modernized Pagination Options (~00:04–00:12)
Before Db2 12, pagination typically required custom logic or application-side filtering. The new features provide more intuitive, LUW-aligned patterns:
- Data-dependent pagination for efficient index-based scrolling
- Numeric pagination using OFFSET and FETCH FIRST n ROWS
- PostgreSQL-style LIMIT / OFFSET syntax
- Optimizer pushdown of ORDER BY and FETCH FIRST for performance
Chris emphasized that while these options enable cleaner code, large offsets still force Db2 to qualify (and discard) many rows, making index-based pagination the more efficient choice.
Controlled Data Maintenance with Row-Limited DELETE (~00:07–00:10)
Chris next covered enhancements that simplify controlled data cleanup. Db2 12 allows fetching and deleting from some rows with:
DELETE FROM table
FETCH FIRST n ROWS ONLY;
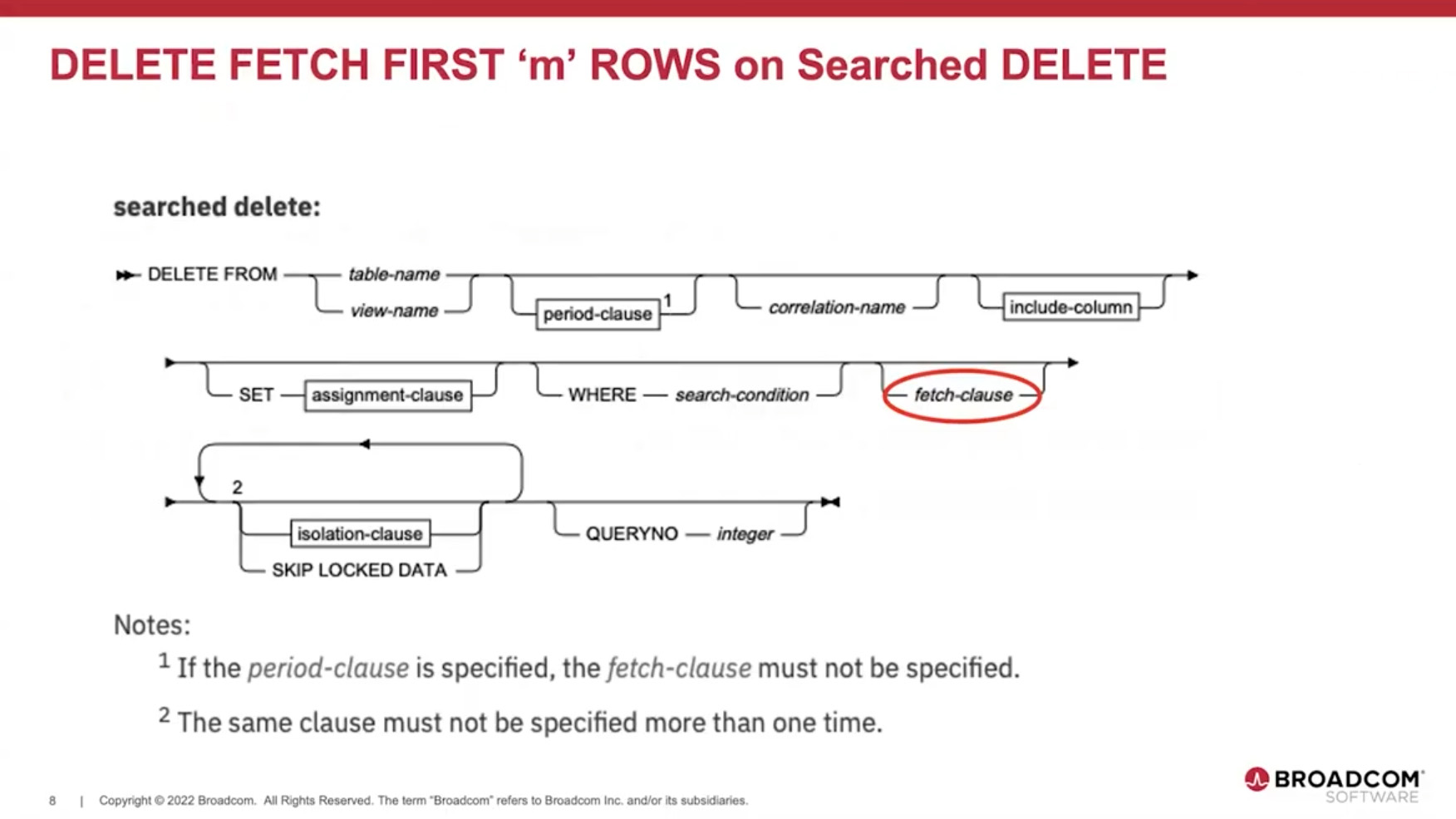
Organizations requested this to perform incremental cleanup using dynamic SQL rather than cursor-based programs. For scenarios requiring repeated commit cycles, Chris noted that autonomous SQL PL procedures—introduced in Db2 11—can perform delete-and-commit loops efficiently within the database.
MERGE Enhancements for Modern ETL Workloads (~00:13–00:20)
The MERGE statement received one of the most impactful updates in Db2 12. Chris explained that Db2 now supports both the version 9 “upsert” MERGE and a more powerful ANSI-compliant MERGE.
Key enhancements include:
- Multiple WHEN MATCHED branches
- Subqueries as MERGE sources
- Flexible logic such as REPLACE, DELETE, SIGNAL, and IGNORE
- Consistent behavior with LUW and other SQL engines
One caveat Chris highlighted: ANSI MERGE does not allow a single source row to update a target row more than once—an intentional standards-based restriction.
New Built-in Functions for Analytics and Data Handling (~00:19–00:25)
Db2 12 delivered a richer set of built-in functions, reducing reliance on custom logic and improving analytical capabilities. Chris outlined several categories:
- Analytics: MEDIAN, PERCENTILE_CONT, PERCENTILE_DISC
- Unique identifiers: GENERATE_UNIQUE_BINARY
- Data integrity: CRC32, MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256
- Bit-string utilities: VARCHAR_BIT_FORMAT
These make Db2 more expressive for statistical workloads and cross-platform interoperability.
SQL PL Enhancements: More Power and Predictability (~00:25–00:40)
Chris described SQL PL as one of the biggest beneficiaries of Db2 12. Before this release, triggers had limited capability and often required stored procedures to perform basic logic. Db2 12 introduces advanced triggers, significantly expanding what developers can express.
Advanced Triggers (~00:26–00:30)
- Full SQL PL support within triggers
- Ability to include logic, branching, variables
- More efficient than calling stored procedures
Trigger Ordering and Versioning (~00:30–00:34)
Db2 now preserves trigger firing order even after updates by allowing:
- CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER
- Multiple versions of a trigger with controlled activation
These enhancements eliminate long-standing unpredictability in trigger behavior.
Chris also covered support for dynamic SQL inside functions (added largely for SAP compatibility) and SQL PL obfuscation, which hides internal logic in shipped routines.
Db2 12 Continuous Delivery Enhancements (~00:35–00:50)
As Chris explained, continuous delivery allowed IBM to ship focused improvements post-GA. These include:
- LISTAG for grouped string aggregation
- UTF-16 casting for SAP
- Temporal auditing behavior fixes
- Encrypt/Decrypt KEY for column-level encryption
- CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE
- Global variable lock controls
- Multi-row INSERT for LUW alignment
Many of these features improve cross-platform SQL consistency and simplify operational workflows.
Db2 13: SQL Data Insights and Next-Generation Features (~00:50–01:06)
Chris shifted to Db2 13, emphasizing that its flagship enhancement—SQL Data Insights (SQL DI)—brings AI-backed capabilities directly into SQL execution. SQL DI allows Db2 to perform tasks such as:
- Similarity scoring
- Clustering and grouping
- Pattern and anomaly detection
- Model-driven transformations
Chris encouraged users to explore the Db2 13 Redbook’s churn prediction example, which demonstrates SQL DI setup, training, and execution using SQL PL procedures.
Other Db2 13 enhancements include:
- Longer column names (>30 bytes) for distributed workloads
- CURRENT LOCK TIMEOUT special register, which must be monitored due to broad accessibility
- Deadlock resolution priority controls
- Improved temporal RI behavior
- INTERPRET function to cast bitstrings
- Expanded PBR ↔ PBG conversion tooling
Conclusion
Chris concluded by reiterating that Db2 12 and 13 reflect IBM’s commitment to delivering more expressive SQL, more powerful procedural logic, greater LUW compatibility, and analytical capabilities enhanced by AI. Together, these enhancements help developers simplify applications, modernize workloads, and maintain high performance on the mainframe.








0 Comments